Dolly preparation for adhesion testing with DeFelsko PosiTest AT adhesion testers
This article discusses the process of dolly preparation necessary for optimal bonding at the dolly-adhesive interface.
In addition, the article covers the importance of proper dolly preparation for maximizing the repeatability of trigger adhesion tests.
Products montioned:
PosiTest AT-A, PosiTest AT-M
Functional principle of the pull-off adhesion test
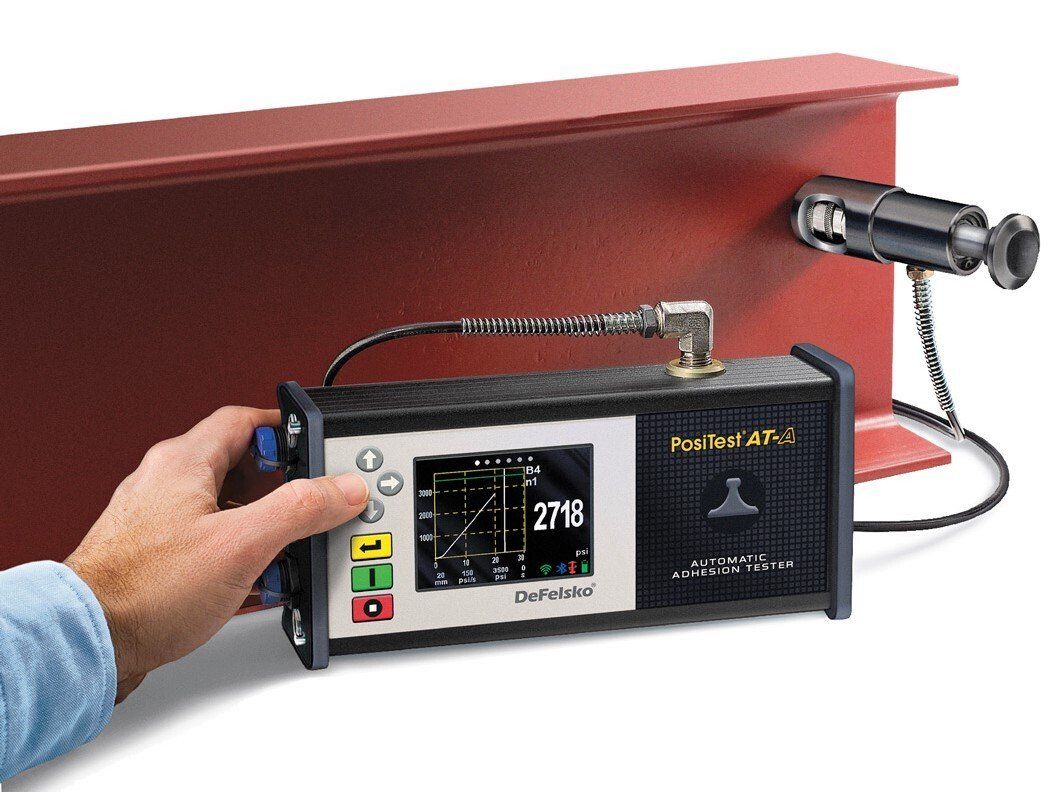
Adhesion testers, such as the PosiTest AT, determine the force required to detach a defined area of coating with a specific diameter from its substrate. This measurement directly reflects the bond strength between the coating and the substrate. By addressing factors that could introduce variability, such as inadequate adhesion between adhesives and poorly prepared dollies, the test results become more reliable and consistent.
The key components of an adhesion tester include a pressure pump, a pressure measuring device (manometer), and an actuator. During testing, the flat surface of a test specimen (dolly) is adhered to the coating being evaluated. Once the adhesive has fully cured, the actuator's coupling piece is secured to the dolly. Gradual activation of the pressure pump increases the pressure within the system. When the applied pressure exceeds the adhesion strength between the coating and the substrate, detachment occurs, and the actuator-dolly assembly separates the coating from the substrate (see Figure 1). The maximum pressure indicated on the device's manometer corresponds directly to the pressure at which the pull-off occurred.
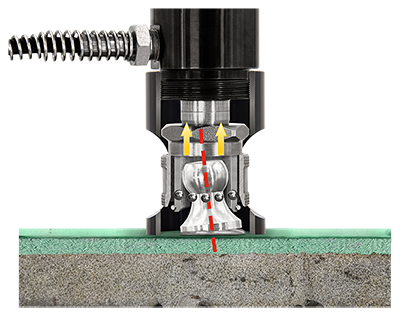
Figure 1: Cross-section of the PosiTest AT actuator
Further details on the exact requirements and the theoretical basis of the pull-off test can be found in the two international standards ISO 4624 "Paints and Varnishes - Pull-off test for adhesion" and ASTM D4541-"Standard Test Method for Pull-Off Strength of Coatings Using Portable Adhesion Testers".
Figures 2 and 3 - mtv messtechnik supplies high-quality DeFelskos devices for adhesion testing, above the PosiTest AT-A Automatic, below the PosiTest AT-M Manual
Preparing the dolly and the surface for the adhesion test
Dollies for pull-off adhesion testers are made from a variety of metals, including aluminum, carbon steel, and stainless steel. While the tests performed in this study focused on the disposable aluminum dollies used with the DeFelsko PosiTest AT Adhesion Tester listed in proposed Appendix A5 of ASTM D 4541 (see Figure 2), the principles discussed apply to all dolly types. Dolly preparation typically consists of three key steps: degreasing, sanding, and cleaning.
Degreasing involves removing oil and grease residues from bonding surfaces, as well as contaminants introduced during handling. Abrasive sanding alters the surface profile of the dolly, achieving two essential goals: increasing the bonding surface area and eliminating oxidation or corrosion layers. Cleaning removes loose particulates, particularly those generated during abrasive processes.
Certain dolly types are pre-machined before shipment, making customer-performed degreasing unnecessary. The machining process, combined with strict handling and packaging protocols, ensures surfaces remain uncontaminated.
Manufacturers supply the necessary equipment, materials, and detailed instructions for preparing dollies for bonding. These preparatory procedures should be informed by rigorous laboratory testing to optimize abrasion and cleaning methods for specific dolly types. Clear, precise, and systematic guidelines ensure consistent and repeatable results across various operators and applications.
Experimental basis for recommending a certain dolly preparation method
The following dolly preparation recommendations have been optimized for the tested adhesion tester in accordance with Annex A5. These recommendations are based on a study of widely accepted methods and subsequent experimental findings. A dedicated experiment was designed to verify and consolidate results from prior tests and comparisons conducted during the product validation phase.
The experiment aimed to directly assess the impact of oxidation and dolly preparation (degreasing, sanding, and cleaning) on adhesion. The methodology involved randomly bonding 48 aluminum dollies to a coated carbon steel plate using a proven adhesive that had been utilized in earlier tests. The study’s objective was to evaluate factors influencing the bond strength between the adhesive and the dolly. To achieve this, a substrate and coating combination with exceptionally high adhesive and cohesive strength was developed to complement the pre-selected Araldite 2011 adhesive. A 4-mil-thick layer of Araldite 2011 was baked onto a ¼-inch carbon steel plate, sourced from a ship’s hull. The steel plate was meticulously prepared by sanding off several millimeters of surface corrosion and contaminants, followed by cleaning with alcohol and a dry cloth. This preparation resulted in a coated substrate robust enough to prevent coating failure during the 48 peel adhesion tests.
The test dollies were evenly distributed across variables including abrasion method, oxidation time, cleaning method, and adhesive cure time. Four abrasion methods were evaluated: machine flattening, end milling, sanding with fine sandpaper, and scrubbing with a Scotch-Brite™ pad. Sanded dollies were exposed to air for three intervals (7 days, 24 hours, and a few minutes) prior to coating application. Before coating, dollies were either wiped with a dry cloth or cleaned with an alcohol-soaked cotton swab followed by a dry cloth. This process yielded two samples for each combination of preparation methods. One sample from each pair was then cured for either 24 hours or 5 days before conducting the pull-off tests.
Results of the different abrasion methods
The results were tabulated for each factor and the average results by abrasion method for each set of 12 dollies are shown in Table 1. As expected, the critical factor for preparation was the abrasion method used. When comparing the results to the abrasion method for the dolly, a predictable pattern emerges. The weakest adhesive bonds were on the machined-only and the finish-milled dollies. These dollies experienced almost 100% adhesive-to-dolly bond failure. This was expected as both preparation methods resulted in relatively smooth surfaces, although the milling process creates large visible grooves in the dolly surface. These grooves increase the surface area of the dollie and are believed to be the reason for the slightly higher bond strength demonstrated prior to failure.
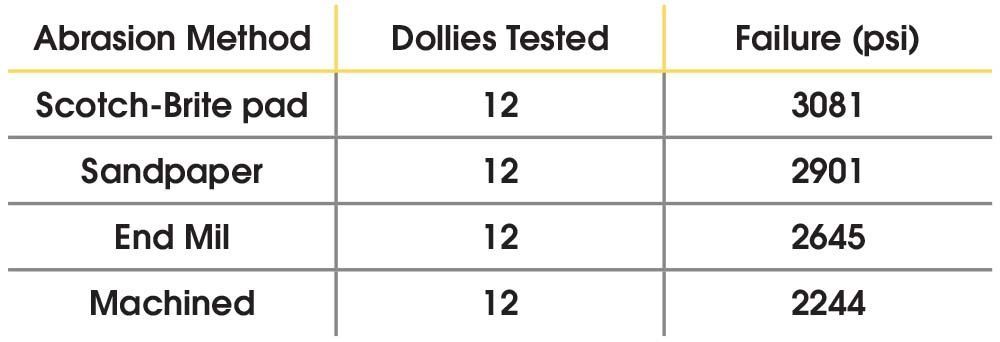
Table 1 - Failure test results related to different abrasion methods
As noted in previous tests, the Scotch-Brite pad achieved the highest overall bond strength, while the sandpaper came in second. Although the visual abrasion results are similar with a Scotch-Brite pad and sandpaper, it is likely that the microstructure (surface profile) is more favorable for adhesion when using a three-dimensional abrasive pad such as the Scotch-Brite. Adhesion requires the adhesive to be soaked into the microstructure through some sort of capillary reaction, so slight changes due to grit or abrasion method can have a significant impact.
Another interesting result was the significantly higher variance between the sandpaper and Scotch-Brite strippings. This result may be related to the rapid buildup of aluminum observed on the surface of the sandpaper, which is difficult to remove between applications. As a result, it is likely that not every dolly will receive the same microstructure. The Scotch-Brite pad allows the aluminum dust to trickle through the fabric, which appears to result in a more uniform microstructure. The Scotch-Brite pad also wears more slowly and needs to be replaced less often.
Results of the oxidation test
The average bond failure based on oxidation time after abrasion is shown in Table 2. This relatively small difference in bond strength is likely due to a limited effect of oxidation on the aluminum dollies. Since aluminum typically forms a thin aluminum oxide layer immediately when exposed to air, it is plausible that uncontaminated dollies would not experience long-term effects of exposure. The effects of oxidation would potentially be significantly greater on other dolly materials, particularly carbon steel.

Table 2 - Results of failure test after a certain oxidation time
Results of cleaning tests
The average bond failure based on cleaning method before bonding is shown in Table 3. This negligible difference supports the theory that by processing the dollies before shipping, degreasing the dollies before use is no longer necessary as long as they are handled carefully by the customer. Bond Failure Based on Cleaning Method
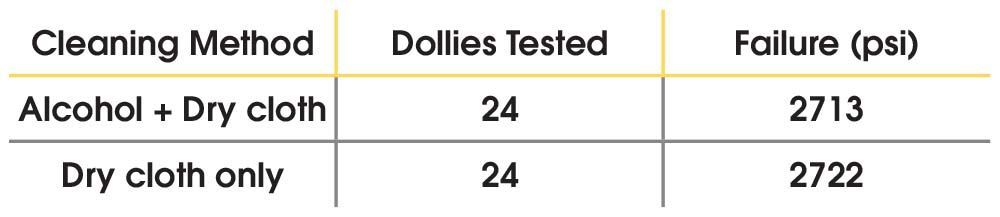
Table 3 – PosiTest AT Dolly Bond Failure Test Results by Cleaning Method
Previous experiments
It is important to point out that the development of hypotheses and the selection and elimination of factors is based on several previous tests, comparisons and experiments. Some of the excluded factors with the corresponding test results are briefly described below.
The effect of shot peened dollies was compared to that of end milling. Three epoxies from different manufacturers were used. A total of 24 dollies were made using the two abrasion methods and then bonded to a highly adhesive, white epoxy coated blasted steel plate. The average fracture strength of the dolly-to-adhesive bond was 2686 psi for the blasted and 2786 psi for the milled dollies. A subsequent literature review helped to explain this result by determining that the expected benefits of shot peening only occur when the dollies are bonded within hours of preparation for coating. 2
It is generally accepted that aluminum that has been anodized and sealed with chromic or sulfuric acid can be bonded after degreasing and light abrasion. Phosphoric acid anodized aluminum has the optimal surface properties for direct bonding without pretreatment, but even the treated dollies must be bonded within a few hours of anodizing to achieve the desired effect.
It is generally accepted that aluminum that has been anodized and sealed with chromic or sulfuric acid can be bonded after degreasing and light sanding. Phosphoric acid anodized aluminum has the optimal surface properties for direct bonding without pretreatment, but the treated dollies must also be bonded within a few hours of anodizing to achieve the desired effect. This theory was tested with a small sample of dollies bonded about a week after anodizing. The delay in bonding the dollies was largely due to the inevitable shipping and handling times. These bond test dollies were also tested against end-milled dollies. The anodized dollies had 20 to 30% lower bond values.
An adhesion test was conducted using an aluminum surface primer to maximize the bond strength of the dollies. The surface primer tested was Henkel Alodine 1132, which was highly recommended as a military approved conversion coating. An equal number of dollies were used for the adhesion test with various abrasion methods including machining, end milling, sandpapering, and shot blasting. In addition, 6 different two-part epoxies were used. The end result was an average bond strength of 1776 psi with Henkel versus 2277 psi without.
This result is likely due to a combination of factors, most notably that the Henkel product, while a highly accepted pressure sensitive adhesive, does not necessarily have the tensile strength required for use in peel testing. It is worth noting that the Henkel product improved peel strength for some combinations of adhesives and abrasion methods, but resulted in lower overall bond strength values.
A final notable comparison involved the degreasing and cleaning of dollies. In summary, dollies that had been sanded and carefully handled did not require any special degreasing and cleaning methods. Whether the dollies were blotted with methyl ethyl keytone, acetone, or alcohol, or simply wiped with a dry cloth, the differences in bond strength were not statistically significant. Dollies that were sanded and then directly bonded without cleaning or degreasing had lower average bond strengths at the dolly-adhesive interface. When examined under a microscope, the adhesive left on the coating from these defects tended to have a higher visible concentration of contaminants on the surface (particularly from abrasion methods such as sanding) when lower bond strength values were observed.
These preliminary results, combined with the prohibitive costs of additional processes such as shot peening, anodizing, conversion coating and degreasing, led to the development of a simple but sophisticated process that is more easily implemented on-site at the customer.
Why is it not recommended to reuse aluminum dollies?
A common customer request that relates directly to dolly reconditioning is the reuse of disposable dollies. This request typically comes from customers who are used to adhesion testers that use the more expensive steel dollies. For such applications, custom-built equipment is offered that allows the customer to remove coating and adhesive from the dolly by heating and time-consuming scraping. The number of times the dolly can be reused is usually only limited by the wear and tear of the dolly surface before each reuse.
From speaking to numerous inspectors, it is clear that they often choose not to reuse the dollies because they need to retain the dollies as important evidence of the inspection results. Other customers choose to retain the dollies as permanent quality records that demonstrate the success of the stripping while also providing related details such as the thickness of the coating stripped. One approach to avoid dolly reuse is to provide a less expensive, disposable dolly that the customer can either retain or discard after the inspection.
If the dolly can be returned to its original condition, it is likely to be safe to use again. However, please note that if the dolly is significantly damaged or worn, reuse is strongly discouraged. This is more common and immediate with aluminum dollies, which can be damaged by the quick disconnect during high pressure pulls. All dolly surfaces may have imperfections caused by repeated sanding or machining when cleaning previous test coatings and adhesives.
conclusions
The experiments, tests and comparisons documented in this article demonstrate that manufacturers must provide the necessary equipment and methods to properly prepare dollies for repeatable bond strength tests. While it is recognized that a variety of chemical and mechanical solutions exist for preparing dollies, it is suggested that simpler and less expensive methods for sanding dollies should exist. In the case of the aluminum dollies studied, sanding with a Scotch-Brite pad followed by cleaning with a dry cloth was more than sufficient to eliminate poor peel adhesion tests due to adhesive failure.
The experimental results briefly mentioned in the article also show that different material and adhesive combinations can have their own optimal preparation methods. The experiments showed that changes in the abrasion method increased the bond strength for one adhesive type, while decreasing it for another. Not all of these alternatives were fully explored, as the preliminary failure strengths for a given adhesive and associated dolly preparation method were still significantly lower.
Because factors such as coating compatibility and cure time may limit the use of a particular adhesive for a particular application, it is recommended that the factors discussed in this article be used as a framework for selecting and verifying customer modifications to the manufacturer's recommended dolly preparation method.
For more information, see our PosiTest AT, Adhesion Testing resources, and dollies.
Please read the PosiTest AT series literature below, this article on measuring adhesion strength with DeFelsko PosiTest AT adhesion tensile tester
and the product descriptions of the respective dollies ( pull stubs ) for PosiTest AT devices with 10 mm, 14 mm and 20 mm diameter.
What is an adhesion test? How does adhesion testing work?
In accordance with ASTM D4541/D7234, ISO 4624 and others, adhesion testers evaluate the adhesion (peel strength) of a coating by determining the greatest tensile force it can withstand before peeling. Failures, evidenced by broken surfaces, occur along the weakest plane within the system consisting of the dolly (loading device, peel nozzle), adhesive, coating(s) and substrate.
The PosiTest AT series of adhesion testers measures the force required to peel a specific test diameter of coating from its substrate using hydraulic pressure.
Why is it necessary to test the adhesion strength?
The objective of adhesion testing is to produce a coating failure. Coating adhesion is an indicator of how well the surface has been prepared and how well the coating has bonded to the surface and/or additional coating layers. Adhesion testing provides a quantifiable method to determine whether a paint or coating system is fit for purpose and can meet the quality requirements of the job specifications.
Choose between Automatic or Manual PosiTest AT Pull-Off Adhesion Testers:
Automatic Pull-Off Adhesion Tester
PosiTest AT - A
- The electronically controlled hydraulic pump automatically ensures a uniform and continuous trigger pressure. Significantly reduces the effort required by the user and the risk of influencing the pulling process.
- Shock- and scratch-resistant color touchscreen with keyboard for operation with or without gloves
- User-adjustable draw speed, draw limit and hold time
- Built-in battery performs over 200 tests per battery charge
- Internal memory stores maximum trigger pressure, trigger speed, test duration, dolly size, pass/fail, type of break, and user notes for 100,000 pull-pull tests in up to 1,000 blocks.
Manual Pull-Off Adhesion Tester
PosiTest AT - M
- Manual hydraulic pump that generates uniform and continuous pressure with a single stroke
- High-contrast, easy-to-read color display
- Traction force indicator for manual monitoring and adjustment of the traction force
- The internal memory stores the maximum trigger pressure, trigger speed, test duration and dolly size for up to 200 triggers
What are the most important steps in conducting a Pull-Off Adhesion tensile bond test / tear test?
- First, please clean the coating and the test stamp (dolly) very thoroughly and sand both the coating and the dolly for better adhesion.
- Apply glue to the dolly and press the dolly onto the surface. Apply glue to the dolly and place it onto the surface.
- Optionally, you can isolate the test area from the surrounding surface by using a core drill bit
- Now the actual deduction test takes place
- Analysis of the test result. Examination and evaluation of the condition of the dolly and the coating, determination of the type of coating breakage

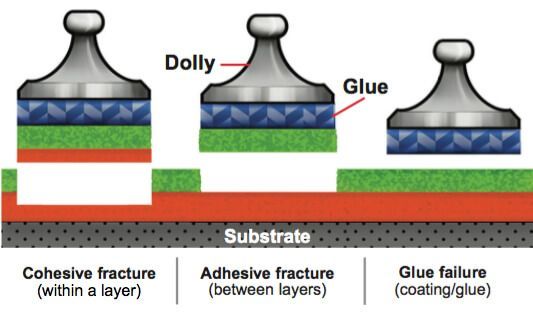
For coatings to perform effectively, they must adhere to their substrates. Several recognised methods, including knife tests and pull-off adhesion testing, measure how well coatings bond. After testing, it’s essential to note whether bond failure was adhesive (at the coating/substrate interface), cohesive (within the coating or substrate), or glue failure (separation within the glue). Many standards, both national and international, require documentation of the fracture type or nature of the fracture.
Determination of the type of coating failure (addition to step 5):
Detailed analysis of the fracture - is it a cohesive fracture, an adhesive fracture or a failure of the adhesive?
Also watch these videos on adhesion testing with the PosiTest AT adhesion tester:
PosiTest AT Automatic adhesion tester from mtv messtechnik
The automatic adhesive tensile tester PosiTest AT offers absolutely uniform tensile force! - No more rejects due to one-sided peeling!
Works without any effort and always delivers exact results. PosiTest AT Automatic Adhesion Tester is used for #tear-off testing
Business hours:
Monday - Thursday from 8:30 a.m. to 5 p.m. and Friday until 3 p.m.









